Application and Advantages of Aluminum Panel Curtain Walls in Modern Architecture

1. Core Applications and Advantages
Lightweight Yet Robust
Aluminum’s high strength-to-weight ratio makes it ideal for large-scale facades. Unlike steel or concrete, aluminum panels reduce structural load on buildings, enabling innovative designs without compromising stability. This characteristic is particularly valuable for skyscrapers and long-span structures where minimizing weight is critical.
Aesthetic Versatility
Architects favor aluminum for its malleability and sleek appearance. Available in a spectrum of finishes—from matte to metallic, textured to smooth—these panels adapt seamlessly to diverse architectural styles. Their ability to be formed into curves, angles, and custom shapes allows for striking visual effects, enhancing a building’s modernity.
Weather Resistance and Adaptability
Aluminum naturally resists corrosion, making it suitable for harsh climates. Its low thermal expansion coefficient minimizes warping under extreme temperatures, ensuring long-term dimensional stability. Additionally, aluminum’s compatibility with insulation materials improves energy efficiency, aligning with sustainable building standards.
2. Challenges: Oxidation, Corrosion, and Aesthetic Degradation
Despite its resilience, aluminum remains susceptible to environmental stressors over time. Common issues include:

Surface Discoloration and Pitting
Exposure to acid rain, saltwater, or industrial pollutants can erode the protective oxide layer on aluminum, leading to white spots, chalky patches, or localized corrosion. These blemishes not only mar the facade’s appearance but may also indicate underlying structural weakening.
Coating and Anodized Layer Failure
Poor-quality coatings or insufficient surface preparation during installation can result in premature peeling, flaking, or delamination. This exposes bare aluminum to moisture and oxygen, accelerating oxidative damage.
3. Consequences of Neglected Corrosion
Compromised Aesthetics
A degraded facade diminishes a building’s curb appeal, affecting property value and tenant satisfaction.
Structural Risks
Severe corrosion can weaken panel integrity, leading to leaks, moisture infiltration, or even panel detachment in extreme cases.
Escalated Maintenance Costs
Reactive repairs—such as replacing damaged panels or repainting entire facades—are far costlier than proactive upkeep.
4. Mitigation Strategies: The Role of Sealant Density
To maximize aluminum curtain wall lifespan, rigorous installation practices and maintenance are essential. A critical factor often overlooked is sealant density during installation.
High-Density Sealant Application
Using high-quality, weather-resistant sealants (e.g., silicone or polyurethane) and applying them at optimal density ensures airtight, waterproof joints. Proper sealing prevents moisture ingress, which is the primary driver of aluminum corrosion.
Regular Inspection and Recaulking
Periodic checks for cracks, gaps, or sealant deterioration are vital. Recaulking every 5–7 years, depending on climate exposure, maintains barrier integrity and aesthetic uniformity.
5. Sustainable and Long-Term Solutions
Material Innovation
Advanced coatings, such as fluoropolymer resins (PVDF) or ceramic-based finishes, enhance corrosion resistance while reducing maintenance frequency.
Integrated Design
Incorporating drainage systems and ventilation cavities behind panels minimizes moisture retention, further mitigating oxidation risks.
Main Causes of Aluminum Panel Oxidation and Rust: Exploring the Role of Density and Other Factors
Aluminum panels are widely used in construction and various industries due to their lightweight, durability, and aesthetic appeal. However, despite their inherent resistance to corrosion, aluminum panels can still experience oxidation and rust under certain conditions. Understanding the primary causes of these phenomena is crucial for effective prevention and maintenance. This article delves into the main factors contributing to aluminum panel oxidation and rust, with a focus on the role of density in these processes.

I. Natural Environmental Factors
1. Rainwater and Acid-Base Erosion
One of the primary culprits behind aluminum panel oxidation and rust is the constant exposure to rainwater, particularly in areas with high levels of air pollution. Acid rain, which contains sulfuric and nitric acids from industrial emissions, acts as a potent corrosive agent. When it comes into contact with the aluminum surface, it accelerates the breakdown of the protective oxide layer, leading to oxidation and rust. The density of the aluminum panel plays a significant role here; denser panels may offer slightly better resistance to acid penetration, but prolonged exposure will inevitably lead to corrosion.
2. Salt Spray Environments
In coastal areas, aluminum panels are particularly vulnerable to salt spray corrosion. The salt-laden air creates a conductive environment on the panel’s surface, promoting electrochemical corrosion. The high chloride ion content in saltwater accelerates the oxidation process, leading to the formation of rust. The density of the aluminum panel influences its susceptibility to salt spray corrosion; while density itself doesn’t directly combat chloride ions, a denser structure can sometimes provide a more robust barrier against initial salt penetration.
3. Ultraviolet Rays and Temperature Fluctuations
Prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation can degrade the protective coatings on aluminum panels, such as fluorocarbon paints. This degradation leads to the formation of micro-cracks in the coating, exposing the underlying aluminum to the elements. Additionally, temperature fluctuations cause the aluminum panel to expand and contract, further stressing the material and coatings. The density of the aluminum panel affects its thermal conductivity; higher-density panels may experience more significant temperature gradients, exacerbating coating fatigue and increasing the risk of oxidation and rust.
II. Material and Process-Related Factors
1. Alloy Composition and Quality Variability
The corrosion resistance of aluminum panels is heavily dependent on their alloy composition. Different aluminum alloys have varying levels of impurities and trace elements, which can significantly impact their susceptibility to oxidation and rust. For example, some alloys may contain higher levels of copper or iron, which can accelerate corrosion. The density of the alloy also plays a part; certain high-strength alloys with increased density may sacrifice some corrosion resistance for mechanical strength.
2. Inadequate Oxide Film or Fluorocarbon Coating
A thin or poorly formed oxide film during the anodizing process fails to provide adequate protection against corrosion. Similarly, fluorocarbon coatings with insufficient thickness or quality can quickly degrade under environmental stress, exposing the aluminum panel to the elements. The density of the oxide film is critical for its protective properties; a denser film offers better barrier properties against corrosive substances, while a porous film may allow them to penetrate more easily.
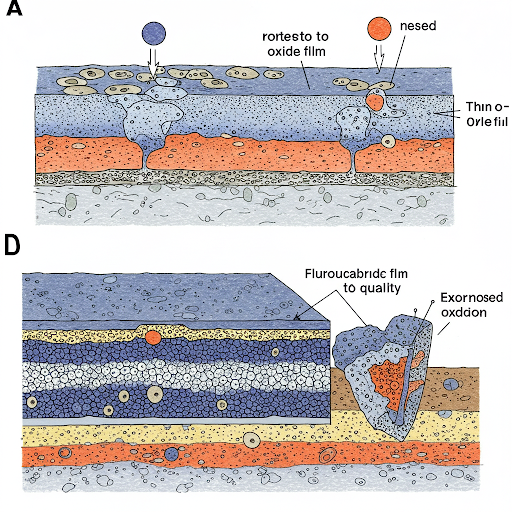
3. Improper Welding and Sealing
Welding and sealing processes, if not executed correctly, can create localized weaknesses in the aluminum panel. These defects act as entry points for moisture and corrosive agents, leading to oxidation and rust. The density of the weld material and surrounding aluminum must be carefully matched to prevent galvanic corrosion between dissimilar metals.
III. Human Factors
1. Surface Damage During Installation
Scratches or dents incurred during the installation process can compromise the protective oxide layer on the aluminum panel, exposing bare aluminum to the environment. This exposed aluminum is highly susceptible to oxidation and rust. The density of the aluminum panel influences its susceptibility to mechanical damage; softer, lower-density panels may be more prone to scratches and dents during installation.
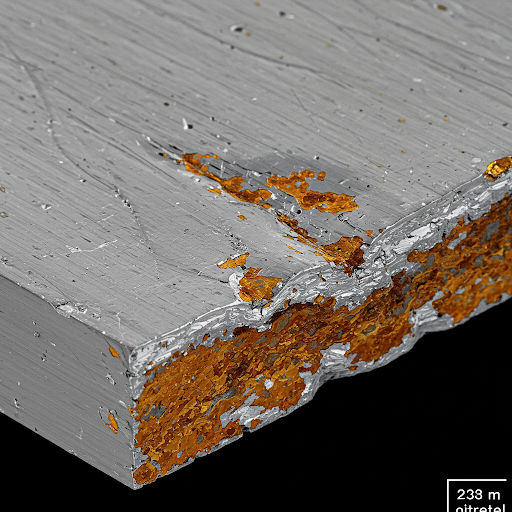
2. Incorrect Cleaning Methods
Using strong acidic or alkaline cleaners can strip away the protective coatings on aluminum panels and etch the aluminum surface. This etching process not only damages the appearance of the panel but also increases its susceptibility to oxidation and rust. The density of the cleaning solution and its contact time with the panel are critical factors in determining the extent of damage.
3. Lack of Maintenance
Regular maintenance is essential for preventing oxidation and rust on aluminum panels. Failure to clean the panels regularly or address minor scratches and dents promptly can lead to more significant corrosion over time. The density of the aluminum panel may influence the frequency of maintenance required; denser panels may be more resistant to corrosion and require less frequent maintenance, but this is not a substitute for proper care.
In conclusion, aluminum panel oxidation and rust are multifaceted issues influenced by a variety of factors, including natural environmental conditions, material and process-related variables, and human factors. Understanding the role of density in these processes can help in selecting appropriate aluminum alloys and coatings for specific applications and environments. By addressing these causes proactively, we can ensure the longevity and aesthetic appeal of aluminum panels in various settings.
Preventing Aluminum Panel Oxidation and Rust: Proactive Design and Material Selection Strategies
Aluminum panels are widely used in construction, automotive, and various industrial applications due to their lightweight, durability, and aesthetic appeal. However, aluminum is prone to oxidation and rust under certain environmental conditions, which can compromise its structural integrity and appearance. To mitigate these issues, a comprehensive approach focusing on material selection, surface treatment, and smart design is essential. This article delves into strategies that prioritize preventing aluminum panel oxidation and rust, ensuring long-term performance and visual appeal.

Alloy Selection and Quality Control
The foundation of any anti-oxidation and rust prevention strategy lies in the choice of aluminum alloy. Opting for high-purity aluminum or alloys with enhanced corrosion resistance is crucial. Alloys such as 5000 or 6000 series, which contain magnesium and silicon, offer superior resistance to corrosion, making them ideal for applications where exposure to moisture and harsh weather is inevitable.
Supplier Credentials and Quality Assurance:
Partnering with reputable suppliers who adhere to strict quality control standards is paramount. Suppliers should provide certifications of material composition, ensuring that the aluminum meets international standards for purity and corrosion resistance. Regular audits and testing of incoming materials can further safeguard against substandard products.
Surface Treatment Techniques
Surface treatments play a pivotal role in enhancing the corrosion resistance of aluminum panels. Three common methods are particularly effective:
Anodizing:
This electrochemical process forms a dense oxide layer on the aluminum surface, significantly improving its corrosion resistance. Anodized aluminum not only protects against oxidation and rust but also provides a durable finish that can be dyed various colors.
Fluorocarbon Coating:
Known for its high weatherability, fluorocarbon coating creates a robust barrier against UV rays, moisture, and pollutants. This makes it a popular choice for exterior applications, such as building facades, where long-term exposure to the elements is a concern.
Electrostatic Powder Coating:
Offering a wide range of color options, electrostatic powder coating provides a decorative and protective finish. While its corrosion resistance may be slightly lower than fluorocarbon coating, it is still a viable option for many applications, especially where aesthetics are a priority.
Structural Design and Node Optimization
Beyond material selection and surface treatment, thoughtful structural design can minimize the risk of aluminum panel oxidation and rust.
Minimizing Water and Dust Accumulation:
Design features that prevent the accumulation of water and dust are critical. For instance, sloped surfaces and drainage channels can direct moisture away from the panels, reducing the likelihood of corrosion.
Considering Thermal Expansion and Contraction:
Aluminum expands and contracts with temperature changes, which can lead to gaps in seals and subsequent moisture ingress. Designing with expansion joints and flexible sealants can accommodate these movements, maintaining a tight seal and protecting against oxidation and rust.
Strengthening Seals and Drainage at Critical Nodes:
Paying special attention to areas such as corners, joints, and interfaces is vital. These critical nodes should be designed with reinforced seals and efficient drainage systems to prevent water from pooling and causing corrosion.
Anti-Corrosion Measures During Aluminum Panel Installation: Combating Oxidation and Rust
The installation process of aluminum panels is a critical phase that significantly impacts their long-term resistance to oxidation and rust. Proper handling and application of anti-corrosion measures during this stage can greatly enhance the durability and lifespan of the panels. This article outlines essential steps and considerations to ensure that aluminum panels remain protected against the elements, focusing on surface preparation, coating application, and sealing techniques.
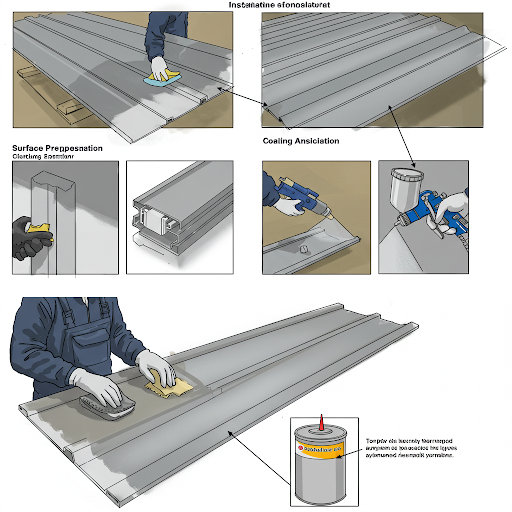
Surface Preparation of the Substrate
The first line of defense against aluminum panel oxidation and rust begins with thorough surface preparation. This involves:
Cleaning:
Prior to any treatment, the aluminum surface must be meticulously cleaned to remove contaminants such as oil, grease, dust, and oxide scales. These impurities can compromise the adhesion of coatings and sealants, leaving the panel vulnerable to corrosion.
Abrading or Polishing:
Once cleaned, the surface should be abraded or polished to create a smooth and uniform texture. This step not only enhances the aesthetic appeal of the panel but also improves the adhesion of subsequent coatings, ensuring a strong bond that protects against moisture ingress and oxidation.
Applying a Primer or Sealer:
Depending on the specific requirements of the project, a corrosion-resistant primer or sealer may be applied to the prepared surface. This base coat provides an additional layer of protection, further shielding the aluminum from environmental factors that contribute to oxidation and rust.
Proper Coating Application
The application of protective coatings is a crucial step in preventing aluminum panel oxidation and rust. Key considerations include:
Coating Thickness and Uniformity:
Ensuring that the coating is applied at the correct thickness and with uniformity across the entire surface is vital. Thin or uneven coatings may fail to provide adequate protection, leaving certain areas of the panel exposed and susceptible to corrosion.
Multi-Coat Application and Curing:
For enhanced durability, multiple coats of the protective coating may be applied, with each coat allowed to cure properly before the next is applied. This builds up a thick, resilient barrier against moisture and other corrosive elements.
Environmental Control:
The coating application process should be carried out in a controlled environment to avoid contamination from dust, humidity, and other factors that could compromise the quality of the finish and the effectiveness of the coating.
Sealing and Waterproofing
Effective sealing and waterproofing are essential to prevent moisture from penetrating the aluminum panels and causing oxidation and rust. This involves:
Selecting Compatible Sealants:
Choosing sealants that are compatible with aluminum is crucial to ensure a strong, durable bond. Incompatible sealants may deteriorate over time, leading to gaps and cracks where moisture can enter.
Quality Sealing Application:
The application of sealants must be done meticulously to ensure complete coverage and adhesion. Any gaps or voids in the sealant can provide pathways for water ingress, increasing the risk of corrosion.
Edge and Corner Waterproofing:
Special attention should be paid to edges, corners, and other vulnerable areas where water can accumulate. Proper waterproofing techniques, such as the use of flashing or specialized sealants, can help prevent moisture from seeping into these areas and causing oxidation and rust.
By implementing these comprehensive anti-corrosion measures during the installation of aluminum panels, you can significantly enhance their resistance to oxidation and rust. From thorough surface preparation to meticulous coating application and effective sealing, each step plays a crucial role in safeguarding the panels against the elements and ensuring their long-term performance and appearance.
Routine Maintenance and Care for Aluminum Panels: Preventing Oxidation and Rust
Proper maintenance and care are crucial for preserving the appearance and integrity of aluminum panels, especially in preventing oxidation and rust. Regular upkeep not only enhances the aesthetic appeal of the panels but also extends their lifespan, ensuring they remain functional and durable over time. This article outlines essential maintenance practices to protect aluminum panels from the elements, focusing on cleaning, inspection, repair, and environmental monitoring.

Regular Cleaning and Inspection
Cleaning Frequency:
The frequency of cleaning aluminum panels depends on their environment. In areas prone to high levels of pollution, such as coastal regions or industrial zones, more frequent cleaning may be necessary to prevent the buildup of corrosive substances.
Cleaning Agents:
When cleaning aluminum panels, it is important to use mild, neutral, or weakly alkaline cleaning agents. Harsh acids or strong alkaline cleaners can damage the panel’s surface, making it more susceptible to oxidation and rust.
Inspection:
Regular inspection of the panel’s surface is essential to identify any signs of damage or wear. Check for cracks, chips, or peeling in the protective coating, as well as any deterioration of the sealants used to waterproof the panel.
Timely Repair and Refurbishment
Addressing Damage:
Any scratches, localized corrosion, or peeling of the protective coating should be addressed promptly. Ignoring these issues can lead to further damage and accelerate the oxidation and rusting process.
Repainting or Refurbishing:
Damaged areas of the panel’s surface can be repaired by repainting or refurbishing. This involves cleaning the affected area, applying a primer if necessary, and then repainting with a compatible coating to restore the panel’s protective barrier.
Replacing Sealants:
Over time, sealants used to waterproof aluminum panels can deteriorate and lose their effectiveness. Regularly inspect and replace any failed or compromised sealants to maintain the panel’s waterproof integrity and prevent moisture ingress.
Environmental Monitoring and Protection
Environmental Factors:
Be mindful of environmental factors that can impact the condition of aluminum panels. Monitor air pollution indices, acid rain levels, and other environmental conditions that could contribute to the corrosion of the panel’s surface.
Protective Measures:
In environments with high levels of pollution or acid rain, additional protective measures may be necessary. This could include applying a protective coating or sealant to the panel’s surface to provide an extra layer of defense against corrosive elements.
By following these routine maintenance and care practices, you can effectively protect aluminum panels from oxidation and rust. Regular cleaning and inspection, timely repair and refurbishment, and environmental monitoring are all essential steps in preserving the appearance and integrity of these panels. With proper care, aluminum panels can maintain their functional and aesthetic qualities for many years.
Common Issues and Solutions for Aluminum Panels: Addressing Oxidation and Rust
Aluminum panels are a popular choice for various applications due to their durability and aesthetic appeal. However, like any material, they can encounter issues over time, particularly related to oxidation and rust. This article addresses some common problems that may arise with aluminum panels and provides practical solutions to help maintain their integrity and appearance.
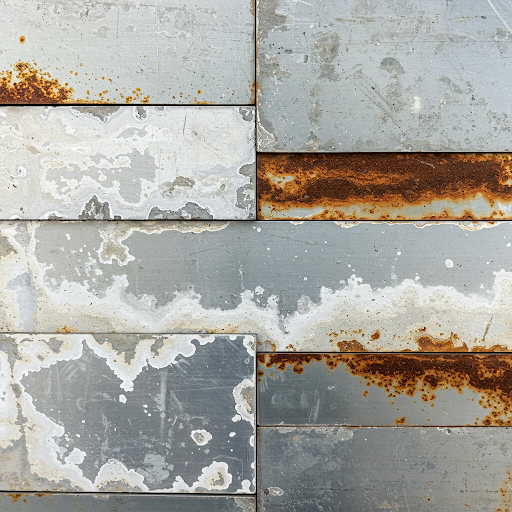

White Spots and Blemishes
Possible Causes:
White spots and blemishes on aluminum panels can be caused by several factors, including water stains, alkaline residues, or poor spraying techniques during the coating process.
Solutions:
To address this issue, the panels should be thoroughly cleaned to remove any dirt, debris, or residues. After cleaning, the quality of the coating should be inspected. If necessary, the affected areas can be repainted or treated with a suitable coating to restore the panel’s appearance and protect it from further damage.
Coating Peeling and Cracking
Possible Causes:
Peeling and cracking of the coating on aluminum panels can occur due to improper construction environments, insufficient coating thickness, or poor adhesion of the coating to the panel surface.
Solutions:
If the coating is peeling or cracking, the affected areas can be sanded down and repainted. In more severe cases, it may be necessary to remove the old coating entirely and apply a new one. This process should be carried out by a professional to ensure the new coating adheres properly and provides adequate protection against oxidation and rust.
Galvanic Corrosion
Possible Causes:
Galvanic corrosion can occur when aluminum panels come into contact with other metals, particularly in the presence of moisture. This type of corrosion is caused by the electrochemical reaction between the different metals.
Solutions:
To prevent galvanic corrosion, it is important to isolate aluminum panels from other metals using insulating gaskets or corrosion-resistant coatings. This will help to break the electrical circuit and prevent the flow of electrons between the metals, thereby reducing the risk of corrosion.
Large-Scale Corrosion Spread
Possible Causes:
Large-scale corrosion spread on aluminum panels can be caused by severe construction defects or a lack of maintenance over an extended period.
Solutions:
If corrosion has spread extensively, it is important to have the panels assessed by a professional team. They can determine the extent of the damage and recommend the appropriate course of action, which may include refurbishing the entire panel or replacing affected sections. Prompt action is crucial to prevent further damage and ensure the longevity of the aluminum panels.
By addressing these common issues and implementing the recommended solutions, you can help to protect your aluminum panels from oxidation and rust. Regular maintenance and inspection are essential to identify potential problems early and prevent them from escalating. With proper care, your aluminum panels can continue to provide a durable and attractive surface for years to come.


