Metal Curtain Wall
Development of Metal Curtain Wall
Since the late 1970s, China’s aluminum alloy doors and windows, curtain wall industry began to start. The popularization, application, and development of aluminum alloy glass curtain walls in construction have experienced the following stages:

- From scratch, from imitation to independent research and development
- From undertaking small-scale engineering construction to large-scale engineering projects
- From producing and constructing medium and low-grade products to manufacturing high-tech products
- From constructing medium and low-rise building doors and windows to constructing high-rise glass curtain walls
- From processing simple medium and low-grade profiles to extruding high-grade profiles with complex cross-sections
- From relying on imports to undertaking foreign projects, achieving rapid development
In the 1990s, new building materials promoted the further development of architectural curtain walls, and metal curtain walls began to emerge nationwide. A metal curtain wall refers to an architectural curtain wall whose panel material is a metal plate. It is essentially a form of glass curtain wall where glass is replaced by metal plates. However, due to differences in surface materials, the two have significant differences in design and construction.
Metal plates offer excellent processing performance, a variety of colors, good safety, and adaptability to complex shape designs. They can be shaped into arbitrary concave and convex lines, processed into curved lines, and provide architects with broad creative space, thus enabling rapid development.
Types of Surface Materials Used in Metal Curtain Walls
The surface materials used in metal curtain walls mainly include the following:
- Aluminum Composite Panels: Composed of inner and outer layers of 0.5mm-thick aluminum panels, with a 2-5mm-thick polyethylene or rigid polyethylene foam panel in the middle. The surface is coated with a fluorocarbon resin coating to form a tough and stable film layer with strong adhesion and durability. These panels come in rich colors and are coated with polyester paint on the back to prevent corrosion. They were commonly used in the early days of metal curtain walls.
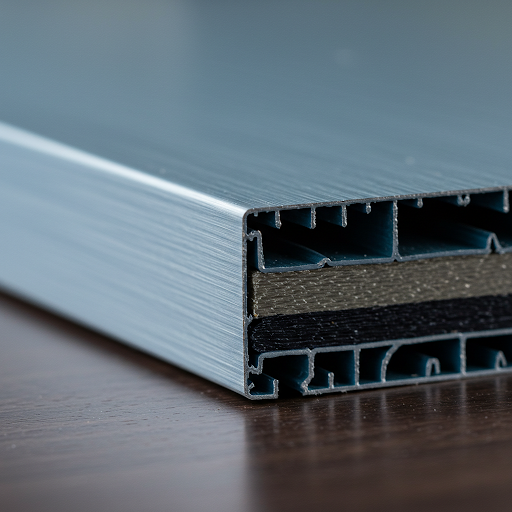

- Single-Layer Aluminum Panels: Made of 2.5mm or 3mm thick aluminum alloy plates. The coating materials and film performance of single-layer aluminum panels for exterior curtain walls are the same as those of aluminum composite panels. These panels are widely used after aluminum composite panels.
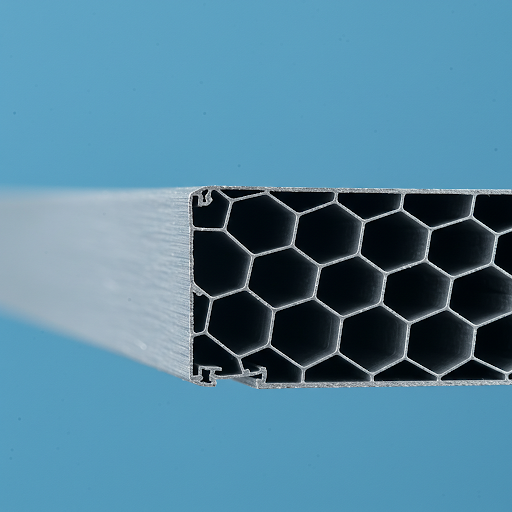
- Aluminum Honeycomb Panels: A composite material made of two aluminum panels bonded to a honeycomb core. Depending on the function and durability requirements of the curtain wall, thicknesses of 10mm, 12mm, 15mm, 20mm, and 25mm can be selected. Aluminum honeycomb panels are commonly used for curtain walls, with various shapes and honeycomb cores requiring special treatment to enhance strength and corrosion resistance. Due to their high cost, they are not widely used.
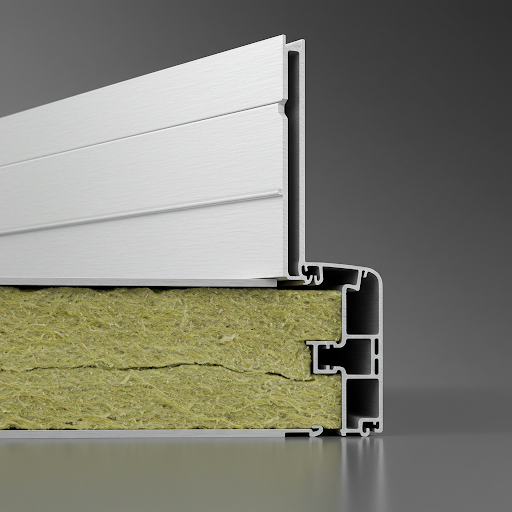
- Aluminum Sandwich Insulation Panels: Similar in form to aluminum honeycomb panels and aluminum composite panels, these panels have an insulation core layer (e.g., rock wool). Because of their high price and the availability of alternative materials that achieve the same effect, their usage is currently limited.

- Stainless Steel Panels: Including mirror, matte, and titanium plates, these panels offer excellent durability and wear resistance. However, thin panels are prone to bulging, while thick panels are heavy and expensive. They are mainly used for local decoration in curtain walls and have limited application.

- Color-Coated Steel Panels: Steel plates with an organic coating, these panels offer good corrosion resistance, bright colors, and easy processing. They retain the strength of steel plates and are low-cost. They are primarily used in industrial and commercial buildings, with limited application in residential construction.
- Enameled Steel Panels: Made of 1.6mm thick very low carbon steel plates, the enamel layer’s glaze expansion coefficient is close to that of steel, making it less prone to warping or bulging. The production process involves cleaning the steel plate, coating it with a glassy mixture powder, and fusing it at 850℃ high temperature. These panels combine the strength of steel plates with glass properties and can be deployed in various colors and patterns. Due to the lack of quality testing, construction norms, and acceptance standards, their application in construction engineering is limited.
The rich decorative surface materials provide broad development opportunities for metal curtain walls.
Leading Products in Metal Curtain Wall
To date, aluminum curtain walls dominate the metal curtain wall market. Their lightweight design reduces building load, making them suitable for high-rise buildings. They offer excellent waterproof, anti-fouling, and anti-corrosion properties, ensuring the building’s exterior remains pristine for a long time. Aluminum curtain walls are easy to process, transport, and install, with a variety of colors and designs that expand architectural creativity. They are cost-effective, easy to maintain, and have a long service life, meeting the needs of building owners and thus enjoying high popularity.
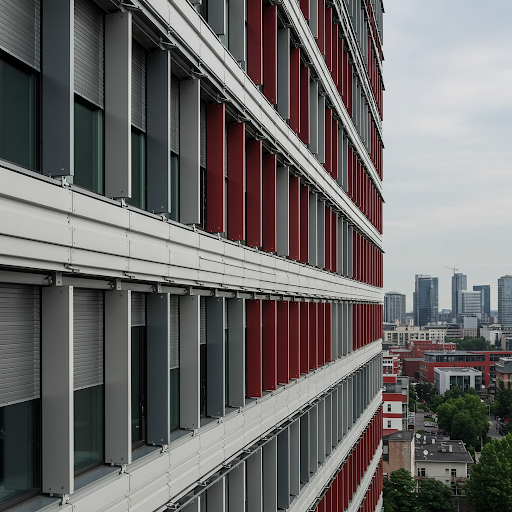

Aluminum Curtain Wall Surface Materials and Performance Comparison
Commonly used surface materials for aluminum curtain walls include aluminum composite panels, single-layer aluminum panels, and honeycomb aluminum panels. The first three are used extensively, with performance differences between them.
Aluminum Curtain Wall Structure Type and Its Advantages and Disadvantages
Aluminum curtain walls are categorized by structure into unitized aluminum curtain walls and stick-built aluminum curtain walls:
- Unitized Curtain Wall: Panels, beams, and columns are assembled into curtain wall units in the factory and installed on-site as units.
- Stick-Built Curtain Wall: Columns, beams, and panels are installed sequentially on-site.
Aluminum Curtain Wall Application Considerations
Material Selection: Strictly inspect materials in the construction market to ensure they meet specifications, standards, and design requirements.
Deformation Resistance: Key parts of the curtain wall system must be scientifically calculated mechanically, considering factors like wind pressure, self-weight, seismic activity, and temperature. Each component must be carefully calibrated to ensure safety.
Panel Connection Method: Floating connections ensure the curtain wall recovers after deformation, maintaining integrity and avoiding surface distortion.
Panel Fixing Method: The fixed-distance compression fixing method ensures panel installation flatness and prevents surface material deformation from uneven force, which could affect appearance.
Composite Panel Material Treatment: The strength of composite panel materials is reduced at folded edges, requiring reliable reinforcement measures.
Reinforcement Setup: Reinforcements on the back of panels must be reasonably spaced and meet strength and stiffness requirements to ensure the functionality and safety of the curtain wall.
Waterproof Sealing: Choose appropriate waterproof sealing methods based on project requirements, such as structural waterproofing, internal waterproofing, or adhesive sealing, to ensure the curtain wall’s functionality and appearance.


